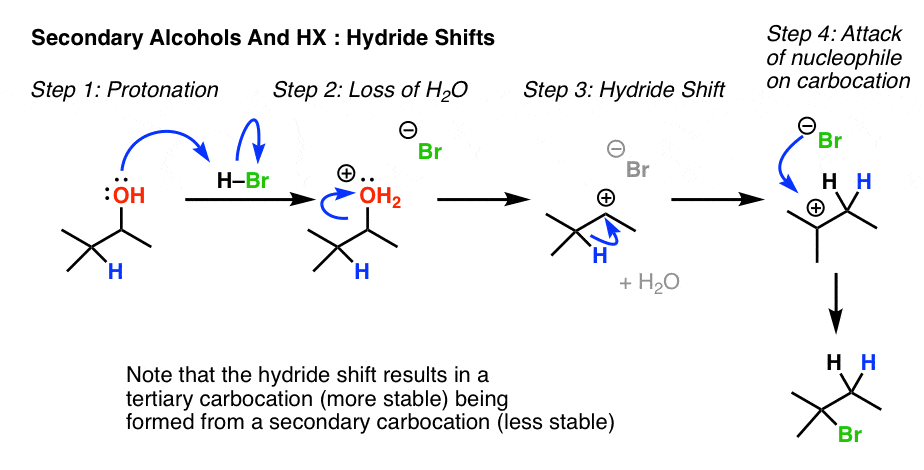
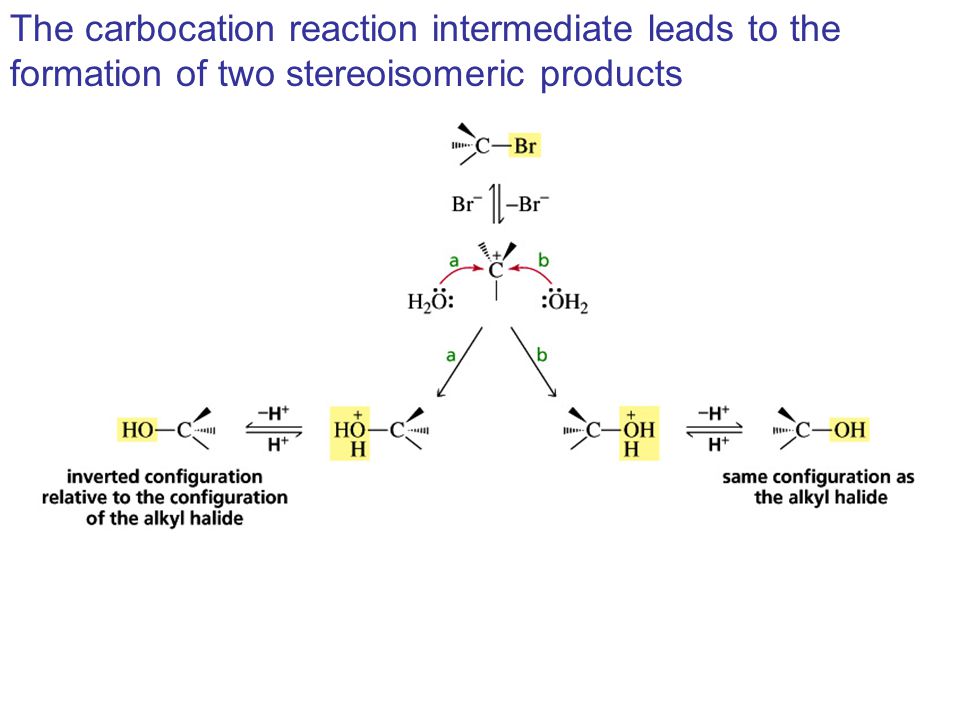
Vinyl Cation Substitution Reaction Mechanism
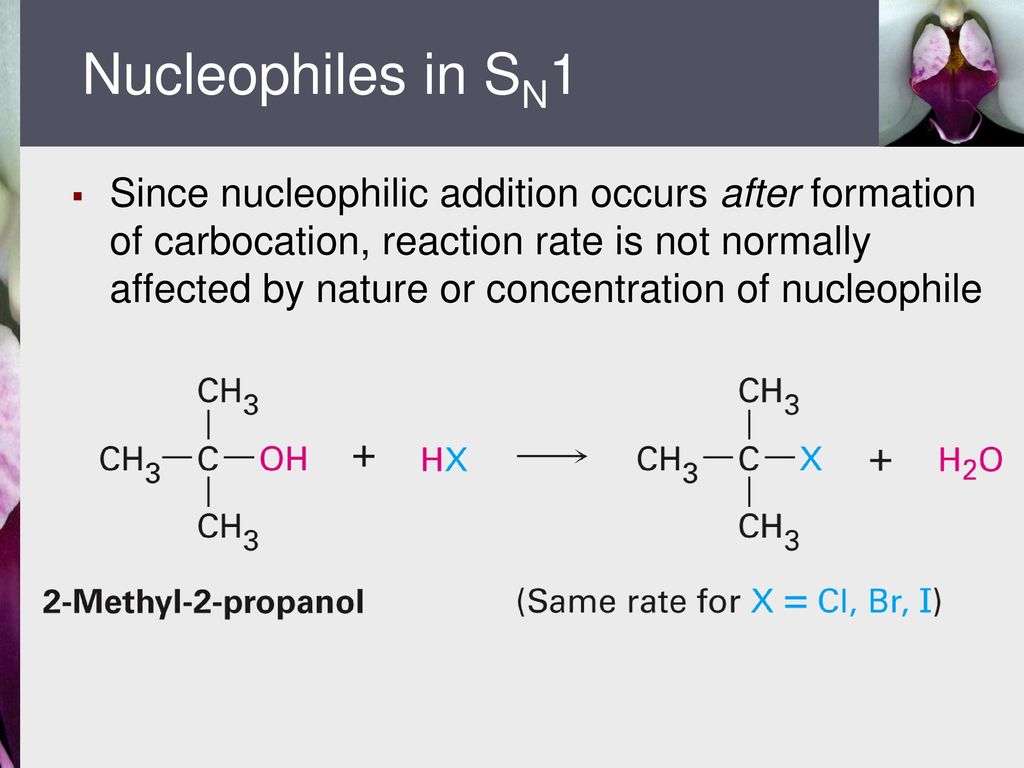
Analogous cations have proven much harder to access from vinylic carbons that are engaged in double bonds.
Vinyl cation substitution reaction mechanism. Based on the reaction mechanism the effects of substitution ring strain and tether length on mechanistic computational amp. The s n 2 mechanism. Saturated carbon centers often undergo substitution reactions by initial cleavage of a carbon halogen or carbon oxygen bond which leaves the carbon positively charged. Chemical society reviews 1998 27 1 81.
Physical organic chemistry in obc. The reactions of the radical cations of vinyl chloride 1 and vinyl bromide 2 with ammonia in the gas phase have been studied by ft icr spectrometry and ab initio molecular orbital calculations. Substitution reaction mechanisms 1. On the other hand williams et al.
Enrico baciocchi giancarlo doddi marcella ioele gianfranco ercolani. 29 32 they found that the reaction of various phenolate ions with 26 scheme 7 29 30 followed a linear relationship on a brønsted plot over a range of pk aroh values above. We first investigated the reaction between terminal propargyl silane 1 a and different sulfoxides in the presence of a brønsted acid. Now show that silicon cations paired with noncoordinating anions can pull triflate groups off such vinylic.
Activation of the ketone by the acid catalyst generates a pentadienyl cation which undergoes a thermally allowed 4π conrotatory electrocyclization as dictated by the woodward hoffman rules. A vinyl cation is a positively charged molecule a cation where the positive charge is located on a vinyl group ch ch2. Other features of the s n 2 mechanism are inversion at the. Its empirical formula is c 2 h 3 more generally a vinylic cation is any disubstituted trivalent carbon where the carbon bearing the positive charge is part of a double bond and is sp hybridized in the chemical literature substituted vinylic cations are often referred to as vinyl cations and understood to.
New synthetic methods via radical cation fragmentation. We set out to direct substitution at either side of the molecule with by using different sets of reagents. Vinyl cation stabilization by silicon enables a formal metal free α arylation of alkyl ketones. Vinyl cations exhibit remarkable reactivity towards arene c h functionalizations.
The hybridization of a vinyl carbocation is sp hybirdized. The vinyl cation is a carbocation with the positive charge on an alkene carbon. The vinyl cations are less stable due to the difference in hybridization of the carbon bearing. This computational study revealed the key mechanistic details of intramolecular c h vinylation through a vinyl cation intermediate.
Carbon with two other atoms attached prefers sp hybridization and a linear geometry. The mechanism of the classical nazarov cyclization reaction was first demonstrated experimentally by shoppe to be an intramolecular electrocyclization and is outlined below. Reported a number of nucleophilic aromatic substitution reactions with concerted mechanisms on substituted 1 3 5 triazines 26 29. Vinyl carbocation is unstable.