Vinyl Halides Nucleophilic Substitution
For 3º halides a very slow s n 2 substitution or if the nucleophile is moderately basic e2 elimination.
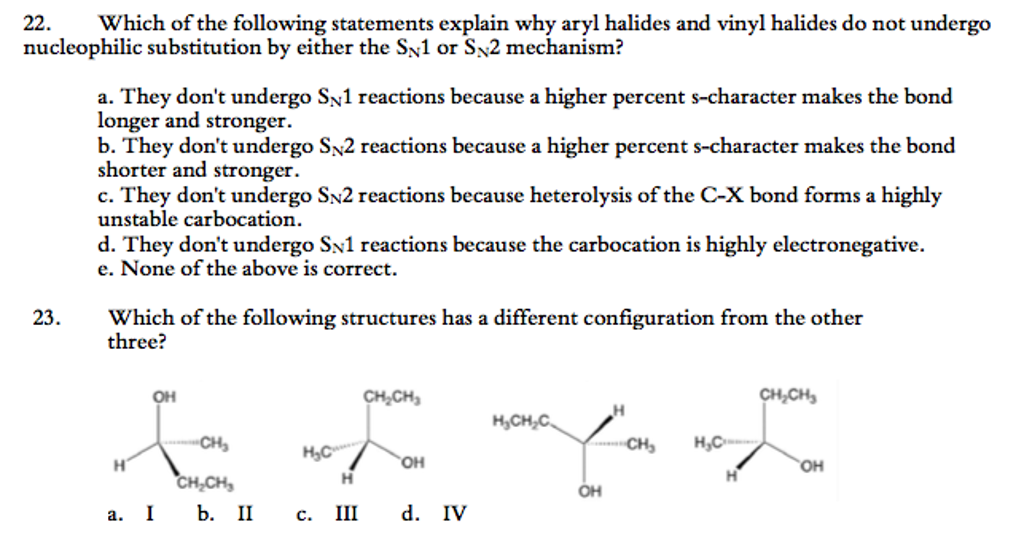
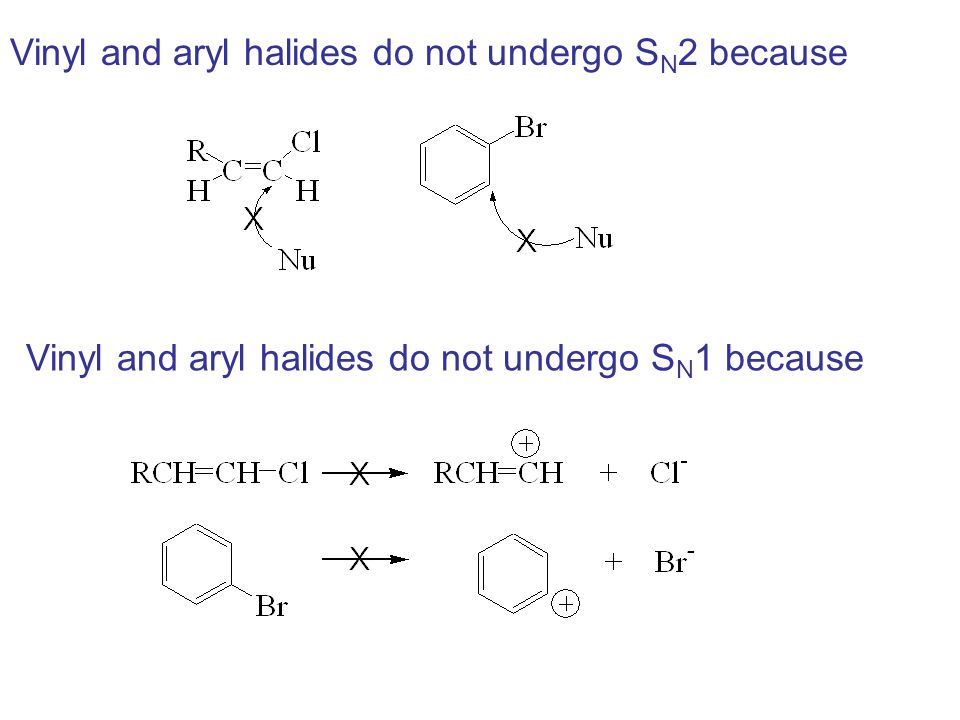
Vinyl halides nucleophilic substitution. Vinylic halides do not show nucleophilic substitution at all because of their stability due to resonance. In high dielectric ionizing solvents such as water dimethyl sulfoxide acetonitrile s n 1 and e1 products may be observed. They don t undergo sn1 reactions because a higher percent s character makes the bond longer and strongei. But elimination to form alkynes is possible.
Aryl halides are relatively unreactive toward nucleophilic substitution reactions. This lack of reactivity is due to several factors. It is possible to replace the chlorine by oh but only under very severe industrial conditions for example at 200 c and 200 atmospheres. In the lab these reactions do not happen.
Nucleophilic substitution at the imidoyl carbon atom. Rapid s n 2 substitution for 1º halides note there are no β. Which of the following statements explain why aryl halides and vinyl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution by either the s 1 or s 2 mechanism. Aryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction as compared to alkyl halides due to resonance stabilization.
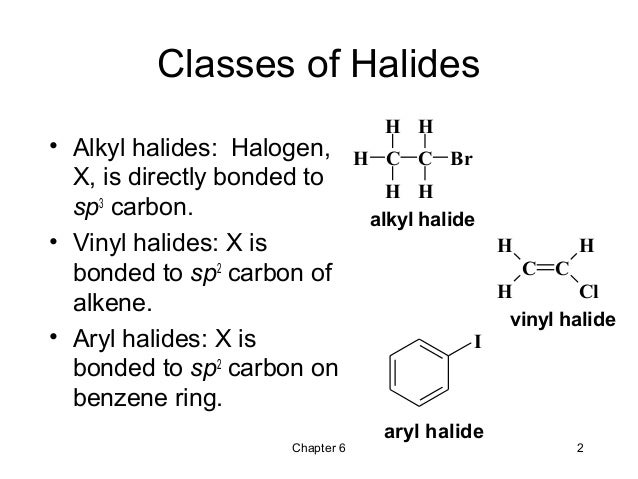
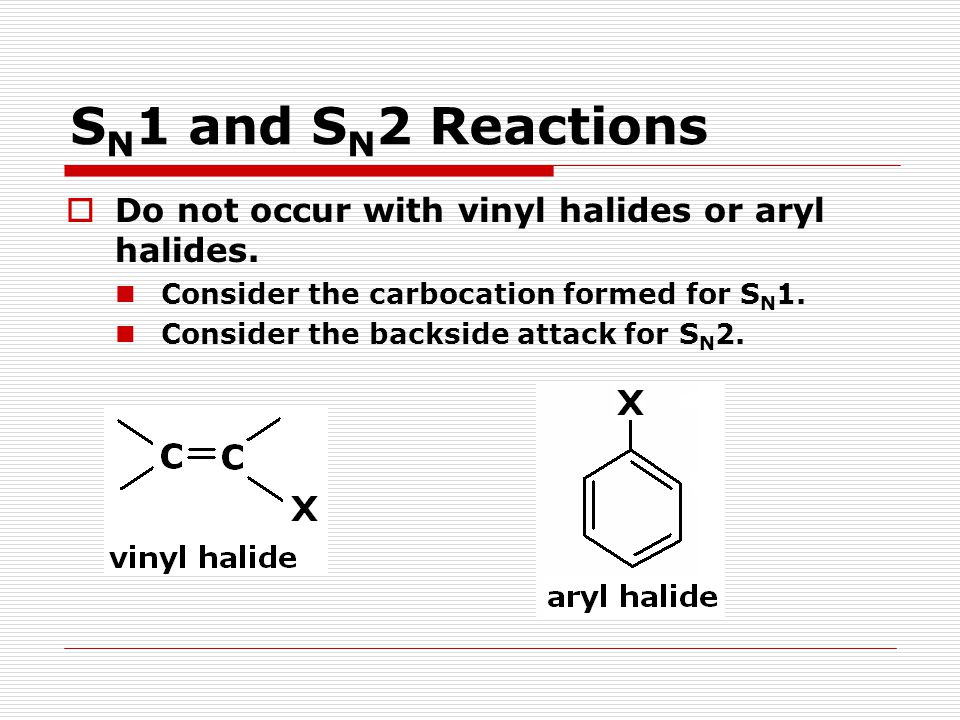
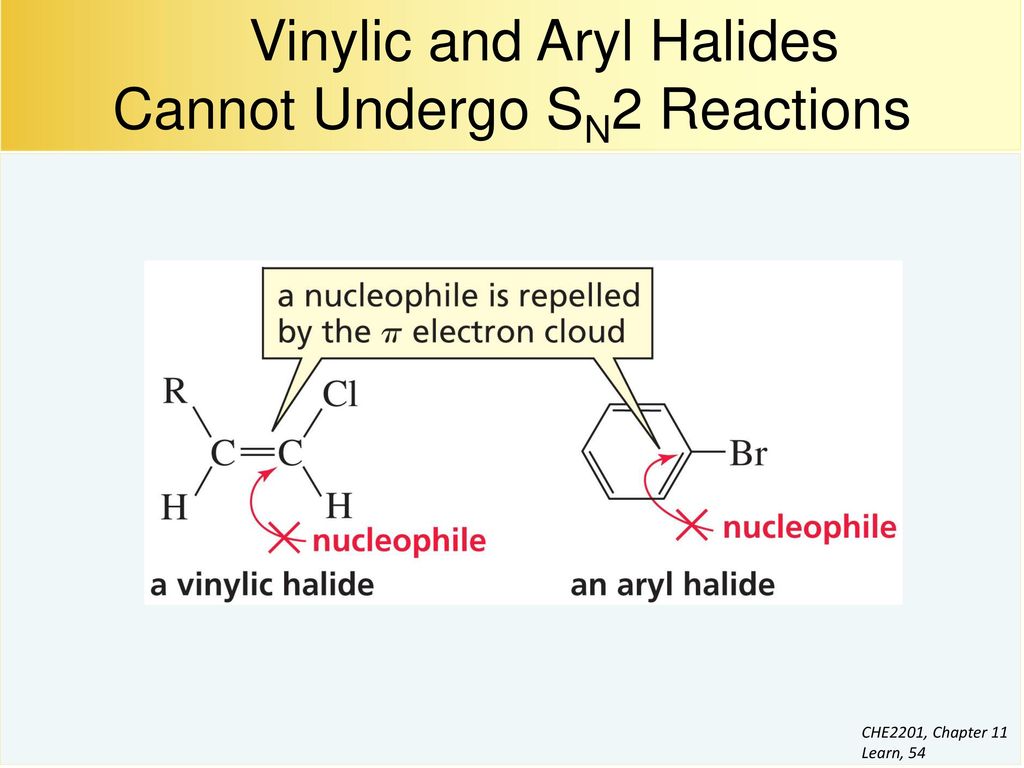
Nucleophilic substitution via the s n 1 or s n 2 mechanism does not generally occur with vinyl or aryl halides or related compounds. Rapid s n 2 substitution for 1º and 2º halides. Under certain conditions nucleophilic substitutions may occur via other mechanisms such as those described in the nucleophilic aromatic substitution article. Likewise phenyl cations are unstable thus making s n 1 reactions impossible.
Steric hindrance caused by the benzene ring of the aryl halide prevents s n 2 reactions. No nucleophile at all can displace the halide ion in a nucleophilic substitution but a strong base suffices for elimination. So the bond between the chlorine and the carbon in the double bond is much too strong stronger than that of an alkyl chloride to be broken by a nucleophile sn2. Nucleophilic substitution via the sn1 or sn2 mechanism does not occur with vinyl chloride or other vinyl halides or aryl halides as it has an unsaturated carbon centre.
Journal of the american chemical society 2001 123 10 2326 2333. In addition the.