Vinyl Halides Wikipedia
In organic chemistry a vinyl halide is a compound with the formula ch 2 chx x halide the term vinyl is often used to describe any alkenyl group.
Vinyl halides wikipedia. For this reason alkenyl halides with the formula rch chx are sometimes called vinyl halides. The name is derived from the latin word for garlic allium sativum in 1844 theodor wertheim isolated an allyl derivative from garlic oil and named it schwefelallyl. It consists of a methylene bridge ch 2 attached to a vinyl group ch ch 2. An allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula h 2 c ch ch 2 r where r is the rest of the molecule.
The most important members are the aryl chlorides but the class of. Generally vinylic halides are unreactive in solution. The choice of aryl halide or pseudohalide substrate sp 2 carbon is one of the factors that mainly influence the reactivity of the sonogashira catalytic system. Consistent with s n 1 chemistry these reactions follow first order kinetics.
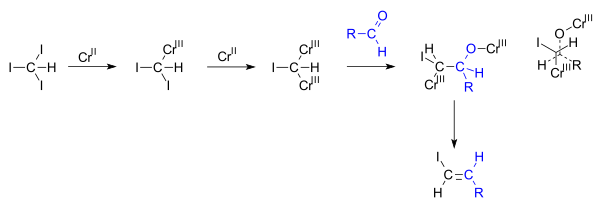
C i bond is the weakest of the halogens the bond dissociation energies of c i is 57 6kcal mol while fluoride chloride and bromide are 115 83 7 72 1 kcal mol respectively. Vinyl halides are common coupling partners in the stille reaction and reactions of this type are found in numerous natural product total syntheses. Vinyl halides are very useful synthetic intermediates due to the vast number of reactions that make use of them. In cross coupling reactions typically vinyl iodides react faster and under more mild conditions than vinyl chloride and vinyl bromide the order of reactivity is based on the strength of carbon halogen bond.
The reactivity of halides is higher towards iodine and vinyl hallides are more reactive than analogous aryl halides. Normally vinyl iodides and bromides are used. In organic chemistry a vinyl halide is any alkene with at least one halide substituent bonded directly on one of the unsaturated carbons. Silver nitrate does not precipitate silver halides in the presence of vinyl halides and this fact was historically used to dispute the existence of the vinyl cation species.
Vinyl chlorides are insufficiently reactive toward oxidative addition to pd 0. In organic chemistry the kumada coupling is a type of cross coupling reaction useful for generating carbon carbon bonds by the reaction of a grignard reagent and an organic halide. From the perspective of applications the dominant member of this class of compounds is vinyl chloride which is produced on the scale of millions of. These include conversion to vinyl grignard reagents elimination to give the corresponding alkyne and.
Aryl halides and pseudohalides. Vinyl cations have been observed as reactive intermediates during solvolysis reactions.